Eliminating the blind spot behind your vehicle can significantly enhance safety during strategies like parking or reversing. Wireless backup cameras offer a clean and convenient way to see behind your car when reversing. Traditional backup cameras rely on a physical cable connection between the camera mounted on the rear of the car and the display on the dashboard.
While effective, this approach can be difficult to install due to the wiring involved. Wireless backup cameras offer a more streamlined solution. Aren’t you curious to know how does a wireless backup camera work?
Weatherproof camera discreetly mounted on your car’s license plate or rear bumper. This camera captures a wide-angle view of the area behind your vehicle. The captured video signal is then converted into a wireless signal and transmitted to a receiver unit located within your car. This receiver unit can be connected to your car’s existing display screen or a dedicated monitor mounted on the dashboard.
The wireless transmission eliminates the need for complex wiring installations, simplifying the setup process. Upon engaging in reverse gear, the receiver unit automatically activates the display, providing you with a real-time view of your surroundings, ultimately promoting safer driving.

Quick Navigation & Previews
Understanding a Wireless Backup Camera
Traditional backup cameras can be a hassle to install due to the long cable runs needed between the camera and the display. Wireless backup cameras offer a more elegant solution, eliminating the wiring mess and simplifying the process. Let’s delve into the inner workings of these convenient systems:
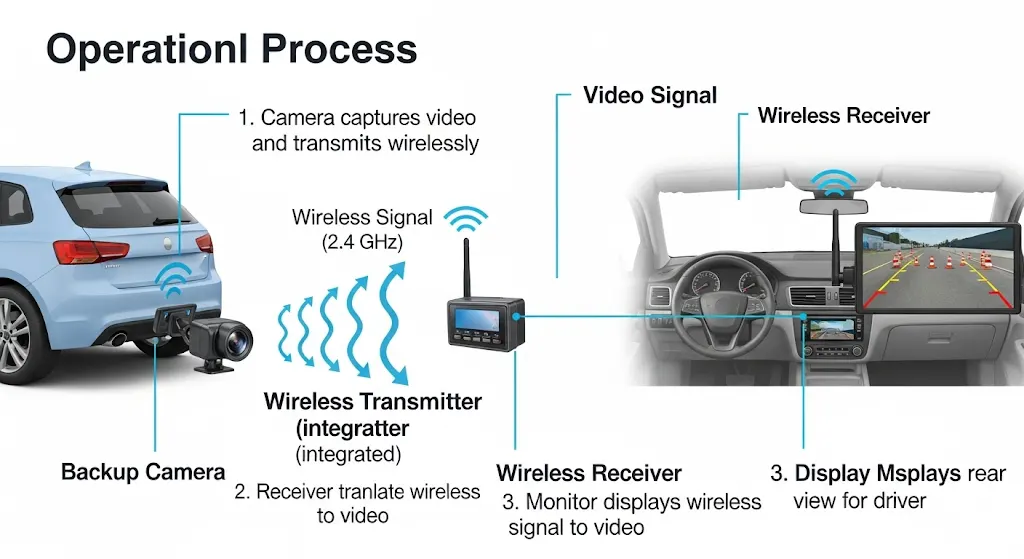
The Watchful Eye: A compact, weatherproof camera is mounted on your car’s rear, typically near the license plate or bumper. This camera acts as your car’s extra eye, capturing a wide-angle view of the area behind the vehicle.
From Sight to Signal: The camera doesn’t directly send images. Instead, it converts the captured video signal into a wireless signal. This allows for a cleaner, cable-free transmission to the receiver unit inside your car.
The Receiving End: A receiver unit, often connected to your existing display screen or a dedicated dashboard monitor, acts as the bridge between the camera and the driver. It receives the wireless signal from the camera and translates it back into a clear image.
Gearing Up for Safety: When you shift into reverse, the receiver unit automatically activates the display. This provides you with a real-time view of your surroundings, helping you navigate tight spaces and avoid obstacles with greater ease.
How Does a Wireless Backup Camera Work?
For decades, traditional backup cameras have served as valuable tools for enhancing rearward visibility. Their installation often requires complex wiring runs from the camera mounted on the rear of the car to the display unit inside the dashboard.
This can be resistant for some drivers, prompting the development of a more streamlined solution: the wireless backup camera system. So let us inform you how does a wireless backup camera work, exploring its core components and functionalities.
The Camera Unit
The foundation of a wireless backup camera system lies in the compact, weatherproof camera unit. Strategically placed on the rear of the vehicle, typically near the license plate or bumper, this camera acts as an extension of the driver’s vision. Equipped with a wide-angle lens, it captures a comprehensive view of the area directly behind the car.
Modern camera units often boast features like night vision for enhanced visibility in low-light conditions and adjustable viewing angles for optimal customization based on the vehicle’s size and shape.
From Light to Wireless Signal: The Conversion Process
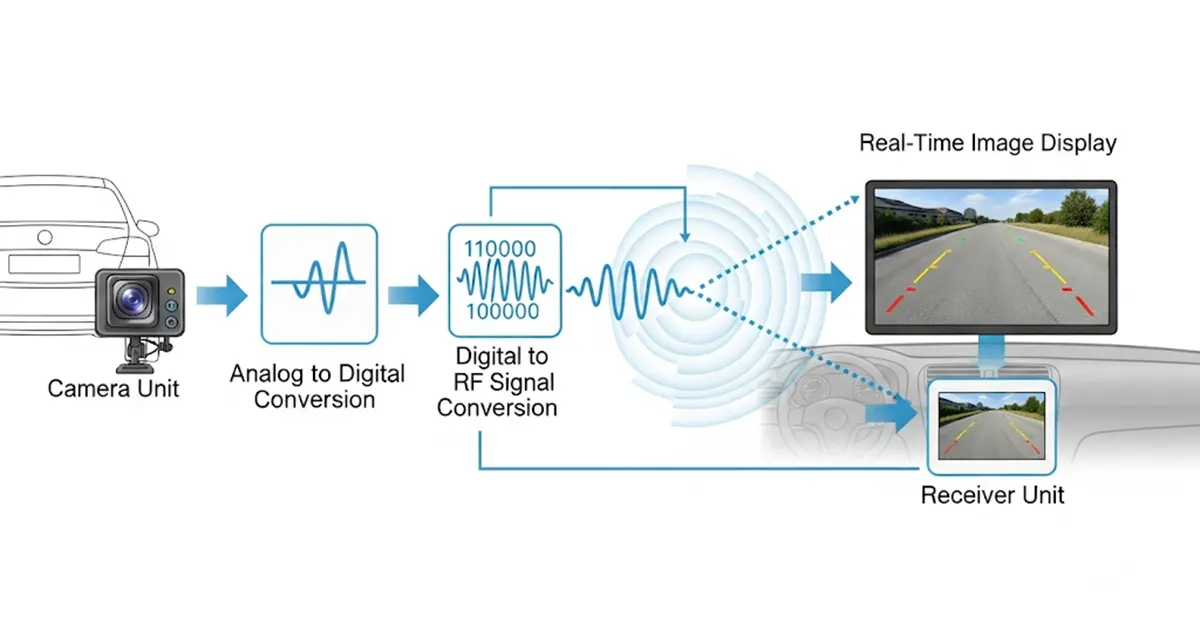
Unlike their wired counterparts that transmit raw video data, wireless backup cameras employ a more efficient approach. The captured video signal undergoes a two-step conversion process. First, it’s converted from analog video data into a digital format. This digital data is then compressed to reduce file size and facilitate efficient wireless transmission.
This compressed digital signal is then further transformed into a radio frequency (RF) signal using a dedicated transmitter within the camera unit. This RF signal serves as the invisible carrier for the video information, readily transmitted through the air without the need for wires.

The Receiving Sector: Bridging the Gap
Inside the car, a receiver unit acts as the crucial bridge between the camera and the driver. This unit can be integrated with the existing infotainment display screen (if compatible) or connected to a dedicated monitor mounted on the dashboard. The receiver unit is equipped with an antenna specifically designed to capture the RF signal transmitted by the camera.
Upon receiving the signal, the receiver unit performs the reverse operation of the camera. It decodes the RF signal, decompresses the data, and transforms it back into a clear and concise video image displayed on the screen.
Seamless Integration with Vehicle Systems
The true brilliance of wireless backup cameras lies in their intuitive integration with existing car systems. Many advanced systems are designed to automatically activate the display unit whenever you shift into reverse gear. This ensures that the crucial rearward view is readily available when you need it most.
Sensors integrated into the car’s reverse light circuit or the gear selector lever itself trigger the activation of the display unit, eliminating the need for manual button presses and ensuring a smooth and intuitive user experience.
Advanced Features
Wireless backup camera technology is constantly evolving, incorporating innovative features that further enhance safety and functionality. Some advanced systems offer distance overlay grids held on the video image, providing a visual reference for estimating the distance between your car and any obstacles behind it.
Additionally, certain systems might integrate with parking sensor systems, providing audible or visual alerts to warn drivers of impending collisions.
Wired vs. Wireless
While wireless backup cameras offer a compelling solution for their ease of installation and user-friendliness, traditional wired systems remain a viable option. Wired systems generally boast a more stable connection and may offer slightly higher video resolution due to the absence of compression involved in wireless transmission.
The installation complexity and potential need for professional assistance can be a deterrent for some drivers.
Advantages of Wireless Backup Camera
Wireless backup cameras are rapidly becoming the preferred choice for drivers due to their focus on convenience. Unlike wired systems that require complex wiring installations, wireless cameras eliminate the need for drilling and messy wires and offer a clean and simple setup process.
This translates to a more aesthetically pleasing car interior and potentially lower costs, as professional installation fees are no longer a factor. Furthermore, wireless cameras provide greater flexibility in placement and allow for optimal positioning based on your vehicle’s size and shape.
With faster setup times and a significant reduction in the risk of wire damage, wireless backup cameras offer a compelling solution for drivers seeking to enhance rearward visibility with a user-friendly and hassle-free approach.
Conclusion
Wireless backup cameras represent a significant leap forward in car safety technology. Their user-friendly approach, streamlined installation process, and ever-evolving features make them a compelling choice for drivers of all levels.
By providing a clear view of the rear surroundings, wireless backup cameras empower drivers to navigate parking strategies with confidence. Avoid unseen obstacles and ultimately contribute to a safer driving experience for themselves and others on the road.
Leave a Reply